How To Become a Data Analyst With No Experience
Starting on the path of how to become a data analyst with no experience might seem difficult, but it is surely possible with the appropriate approach and determination. In today's data-driven world, there is a growing demand for professionals who can understand and extract insights from massive databases. Whether you are transferring from another area or entering the workforce for the first time, a career in data analysis provides several prospects for advancement.
In this article, we'll lead you through the process of becoming a skilled data analyst, even if you're beginning from zero. From understanding the position to earning the essential skills and certifications, we've got your back. Learn how to get started in data analysis with our helpful guide designed to help you succeed. Let's plunge in!
What is a Data Analyst?
A data analyst plays a critical role in evaluating data to influence organizational choices. Their position includes methodically gathering, refining, analyzing, and visualizing data to gain significant insights.Data analysts are vital in a variety of industries, including banking, healthcare, and marketing, where they make substantial contributions to improving operational efficiency and stimulating innovation. Their ability to translate raw data into useful insight helps them comprehend market trends, and customer behavior, and optimize corporate operations.
In the modern data-driven world, data analysts play critical roles in helping firms remain competitive, adapt to market changes, and capitalize on growth possibilities. They act as strategic partners by leveraging the power of data, allowing organizations to make educated decisions and achieve long-term success in the digital age.
What Does a Data Analyst Do?
It is a dynamic process that includes data collecting, statistical analysis, report generation, and insight transmission. Attention to detail, problem-solving skills, and the ability to convey stories with data are all required for success in this profession.Every day provides new difficulties for data analysts to uncover meaningful insights that drive educated decisions. They play critical roles in areas including banking, healthcare, and marketing, optimizing operations, and forecasting trends.
Data analysts use complicated datasets to affect the direction of enterprises and sectors. Are you interested in learning more about data analytics? Discover the complexities of this critical function and how it may transform your organization's success.
How To Become a Data Analyst With No Experience?
Becoming a data analyst is highly possible, but it may need effort, self-learning, and perseverance. Here's an easy guide to get you started on how to become a data analyst with no experience:#1. Research the Field
Understanding the complexities of data analysis is essential for anybody seeking to be a data analyst. Discover what data analysts do daily, their position in various businesses, and the skills they use.By thoroughly researching the industry, you will obtain an understanding of the sorts of activities you will be expected to complete as well as the tools you will need to learn. This core information will assist you in setting realistic goals and creating a targeted learning strategy.
Furthermore, studying industry trends and the need for data analysts in various industries will help you make career decisions and plan your job search approach.
#2. Learn Basic Data Analysis Concepts
To succeed as a data analyst, you must have a thorough knowledge of core data analysis ideas. This involves knowing various data kinds including numerical, categorical, and ordinal data, as well as metrics of central tendency and dispersion.Learning about data visualization strategies and how to effectively convey findings using graphs and charts is also essential. Furthermore, mastering fundamental statistical concepts such as hypothesis testing, probability distributions, and correlation sets the framework for sophisticated analytic approaches in the future.
#3.Master Data Analysis Tools
Proficiency in data analysis tools is a must for aspiring data analysts in today's data-driven environment. Because of their adaptability and abundance of libraries for data manipulation, analysis, and presentation, Python and R are two computer languages that are often used in the area.Similar to how Excel is still a mainstay for simple data operations and presentation, SQL (Structured Query Language) is necessary for searching and extracting data from databases. Gaining proficiency with these technologies will enable you to manage a variety of data analysis jobs and make valuable contributions to projects across several industries.
#4. Develop Statistical Knowledge
Statistics is the foundation of data analysis, providing the theoretical basis for analyzing data and reaching meaningful conclusions. A solid background in statistics is required for each prospective data analyst.This involves knowledge of probability theory, hypothesis testing, regression analysis, and other statistical techniques typically used in data analysis. Statistical expertise helps data analysts make educated judgments, detect data patterns and trends, and generate actionable insights that drive business outcomes.
By devoting time to studying statistics and its applications in data analysis, you will get the analytical abilities required to flourish in the area and face challenging data analysis issues with confidence.
#5. Work on Personal Projects
To improve your data analysis talents and create a portfolio that impresses employers, you need to get practical experience. Assist yourself in real-world circumstances by taking on personal data analysis projects that correspond with your objectives and areas of interest. Working on personal projects lets you show off your creativity, problem-solving abilities, and capacity to extract useful insights from data.Examples of these projects include examining patterns in healthcare data, forecasting housing prices using historical data, and analyzing trends in social media data. Completing personal projects also demonstrates your expertise and dedication to data analysis in a concrete way, which might set you apart from other job applicants.
#6. Build a Portfolio
A well-crafted portfolio is vital for demonstrating your talents and expertise as a data analyst, especially if you are new to the industry. Documenting your projects, academic courses, and any related internships or volunteer activities in a portfolio demonstrates your knowledge of data analysis methodologies, programming languages, and data presentation tools.Include full explanations of each project, such as the issue statement, methodology, important results, and visualizations developed. A visually beautiful and well-organized portfolio not only demonstrates your technical skills but also your ability to effectively explain difficult ideas. Whether you're looking for internships, entry-level roles, or freelancing possibilities, a great portfolio can help you obtain your dream job in data analysis.
#7. Network with Professionals
One of the most effective ways to progress your data analysis job is through networking. Make connections with industry professionals by using data science forums, industry-specific groups, and internet platforms such as LinkedIn.Participate in conversations, impart your knowledge and perspectives, and ask seasoned professionals for guidance. In addition to keeping you informed about employment openings and industry trends, networking offers professional growth and mentorship possibilities.
Go to conferences, meetings, and industry events to grow your network and make contacts with other industry experts. You could also think about contacting individuals in your town or former students from your college who may help you along the way as you pursue a career in data analysis.
#8. Seek Feedback
Receiving constructive criticism is crucial for developing as a data analyst. Never be afraid to ask peers, mentors, and industry professionals for input on your projects, portfolio, and technical abilities.Look for chances to show off your work and get input from more seasoned professionals. To improve your abilities and showcase your work, pay close attention to their advice and use constructive criticism.
Getting feedback indicates your openness to learning and wanting to advance as a data analyst, in addition to assisting you in identifying areas for growth. Accept criticism as a priceless teaching tool, and use it to improve your data analysis abilities over time.
#9. Take Online Courses
An easy and accessible approach to expanding your understanding of data analysis and learning new skills is through online tutorials and courses. Enrol in courses from respectable websites like Coursera, edX, Udemy, and DataCamp.These platforms offer thorough coverage of topics related to data analysis, from fundamental ideas to sophisticated methods. Select courses that fit your interests and learning objectives, then set aside time to finish them at your speed. To help you learn and make sure you understand the material, a lot of online courses include interactive quizzes, real-world projects, and practical exercises.
Additionally, to strengthen your resume and show prospective employers your competence, think about obtaining specialized certifications in fields like data science, machine learning, or data visualization.
#10. Participate in Data Challenges
Participating in data analysis challenges and contests on platforms such as Kaggle is an excellent way to expose your talents to the test, network with other data lovers, and present your work to the wider data science community.By taking part in data challenges, you may solve complicated issues, use your skills in real-world situations, and become familiar with various processes and tools for data analysis. Data challenges offer an individual or team-based platform to showcase your ingenuity, problem-solving abilities, and capacity to extract valuable insights from data.
Gaining recognition as a successful data analyst and drawing interest from companies looking to hire the best candidates in the industry are two other benefits of winning or placing well in data challenges.
#11. Apply for Internships
Internships provide significant experiences in the data analysis sector, including exposure to industry professionals, professional mentorship, and hands-on training. Numerous businesses provide internships intended especially for students and new graduates wishing to launch data analysis careers.Seek internships with businesses that fit your interests and professional objectives in a variety of fields, such as technology, finance, healthcare, e-commerce, and consulting.
Through internships, you may put your academic knowledge to use in practical situations, work on worthwhile projects, and acquire marketable skills and competencies.
Furthermore, internships offer chances to network with industry experts, get mentorship from seasoned professionals, and investigate other career options in data analysis.
#12. Stay Updated
The field of data analysis is frequently growing, with fresh tools, technologies, and approaches appearing at breakneck speed. To remain successful in the sector, you must stay up to speed on the newest data analysis trends, innovations, and best practices.To remain up to date on industry improvements, follow professional blogs, podcasts, and publications, attend meetings, webinars, and seminars, and network with thought leaders and practitioners in the area.
Additionally, look for possibilities for professional growth regularly, whether it's taking advanced courses, attending training sessions, or acquiring industry certifications. You'll establish yourself as a skilled and in-demand data analysis specialist by remaining proactive and up to speed on industry trends and breakthroughs.
#13. Volunteer for Non-profit Projects
Applying your knowledge and improving society at the same time may be gratifying when you volunteer your data analysis abilities to community projects and nonprofits. There's a chance for data analysts to use their abilities for social good because many non-profit organizations lack the means and knowledge to analyze their data properly.Engaging in volunteer work enables you to enhance your skills, build your resume, and contribute significantly to your community. You can analyze program results, gather statistics on fundraising, or spot demographic patterns.
Furthermore, volunteering offers chances to expand your professional network within the non-profit industry, establish connections with local stakeholders, and exhibit your dedication to using data for social transformation.
#14. Attend Workshops and Conferences
Professional networking, learning from industry experts, and being up to date on the newest trends and developments in data analysis are all made possible by attending workshops, conferences, and seminars. Seek conferences and workshops centered on data science, machine learning, data analysis, and related disciplines.Attend sessions that cover a broad variety of topics, from industry applications and best practices to technical skills and approaches. To enhance your comprehension of important ideas and obtain knowledge about new trends and technology, interact with presenters, pose questions, and take part in conversations.
Additionally, make the most of networking opportunities to get in touch with industry leaders, exchange experiences, and ask more seasoned practitioners for guidance and mentoring.
#15. Be Persistent and Patient
Resilience, endurance, and patience are necessary for establishing a prosperous career in data analysis. It's critical to remain dedicated to your educational path in the face of obstacles or disappointments.Recognize that learning data analysis techniques requires patience and persistence and that results are not always consistent. Adopt a growth mentality, see setbacks as chances for improvement, and recognize your accomplishments along the route.
By establishing reasonable objectives, monitoring your advancement, and asking for help from peers, mentors, and the larger data science community, you can maintain your motivation. Keep in mind that every obstacle you go over and every task you do will help
you get one step closer to realizing your professional aspirations as a data analyst.
What Data Analyst Skills Needed To Get a Job?
To succeed as a data analyst, you must develop a strong balance of technical competence and soft abilities. Let us go out about what each category comprises.
#Technical Skills
1. Proficiency in Programming Languages
Skill in language programming such as Python and R is necessary for data analysts. With the adaptability these languages provide, analysts can effectively handle difficult analytical tasks including statistical analysis, machine learning algorithm implementation, and data manipulation.2. Data Manipulation and Querying (SQL)
A strong grasp of SQL is required for effective data analysis. SQL competence helps analysts extract, modify, and manipulate data from databases, allowing for extensive analysis and insight production from a variety of datasets.3. Statistical Analysis
Data-driven decision-making relies heavily on statistical analysis. Data analysts must have a thorough grasp of statistical methodologies to use relevant approaches for hypothesis testing, regression analysis, and correlation studies, therefore revealing insights and patterns within the data.4. Data Visualization
Effective data visualization is critical for communicating insights. Proficiency in data visualization technologies enables analysts to develop engaging charts and graphs that help stakeholders grasp complicated data linkages and patterns, allowing for more informed decision-making.5. Machine Learning Concepts
Understanding how machines learn is crucial in the big data era. Comprehending diverse machine learning algorithms enables analysts to construct prognostic models, categorize information, and reveal concealed patterns, so yielding practical insights for the triumph of organizations.#Soft Skills
1. Strong Analytical Skills
To analyze complicated datasets and extract valuable insights, data analysts need to possess strong analytical skills. These abilities include the capacity to solve problems, observe patterns, and extrapolate insights from data to inform business choices.2. Attention to Detail
Reliability and accuracy in data analysis are ensured by attention to detail. To preserve the integrity of conclusions and inspire confidence in stakeholders, analysts carefully examine data, spot abnormalities, and put quality control procedures in place.3. Critical Thinking
To evaluate facts objectively and make data-driven judgments, critical thinking is essential. Analysts do thorough information analysis, test presumptions, and unearth patterns that fuel innovation and advancement in businesses.4. Problem-Solving Abilities
An analyst's ability to solve problems effectively allows them to take on difficult problems and achieve their goals. Analysts provide value to the company by utilizing data to generate solutions that are identified, investigated, and implemented in practice.5. Effective Communication
Clear sharing of findings is critical for data analysts. They must transform technical results into practical recommendations, tailoring their communication approach to diverse audiences, to guarantee team comprehension and participation.6. Teamwork
For data analysis efforts to be successful, collaboration is essential. Data analysts work in cross-functional teams with various specialties to overcome obstacles, exchange information, and provide superior insights that promote organizational performance.Important Data Analyst Certification
Certifications can improve your reputation and marketability as a data analyst, while they are not necessarily required. Think about getting certified in areas like:1. Azure Data Scientist Associate
The sophisticated tools and services offered by Microsoft Azure are used to demonstrate your competency in data science activities, as attested by this certification. Your capacity to use cloud platforms for advanced data analysis solutions is validated.2. Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate
This certification, provided by Google, gives you crucial skills for data analysis jobs. It includes important topics such as data collection, cleaning, analysis, visualization, and interpretation with the help of Google Analytics and other pertinent technologies.3. IBM Data Analyst Professional Certificate
This IBM-designed certification focuses on developing practical data analysis abilities with IBM's state-of-the-art tools and techniques. To help you extract meaningful insights from data, it includes machine learning with Python, SQL for data science, Python for visualization of information, and data science machine learning.4. Tableau Desktop Specialist
With a focus on displaying data effectively, this certification proves your mastery of Tableau, a popular application for producing engaging and intelligent representations. It demonstrates your proficiency in creating diagrams, interacting with data, and successfully conveying insights.Secret Ideas To Improve Chances of Getting a Job as a Data Analyst
Ready to begin your career as a data analyst? Here are some secret ideas to increase your chances of getting your desired job:1. Master Excel Tricks
Excel knowledge is an important advantage for data analysts, complementing programming abilities. Explore sophisticated capabilities such as VLOOKUP, INDEX-MATCH, and pivot tables to speed up data manipulation and analysis. Mastering these tasks demonstrates your ability to manage data effectively and provide high-quality analysis, which is extremely appealing to future employers.2. Embrace Data Visualization
Effective presentation of data is critical for communicating insights to stakeholders. Mastery of tools like Tableau or Power BI enables the production of visually appealing dashboards that go beyond simple charts. This competency improves insight communication, making your findings more impactful and actionable for decision-makers across the organization.3. Become a Storyteller
Beyond statistics, data analysis entails creating tales that connect with audiences. Develop narrative abilities to contextualize results within corporate objectives, making analysis more relevant and practical. By developing narrative skills, you may increase the relevance of your findings and promote yourself as a valued adviser inside the organization.4. Build Domain Knowledge
Working as a data analyst necessitates a thorough grasp of the industry or topic. By immersing yourself in its difficulties and tendencies, you may give specific insights that significantly enhance your analysis.5. Stay Curious
Develop an inquisitive mentality to investigate new datasets and analysis methodologies. Curiosity drives creativity, allowing you to discover hidden insights and broaden your analytical talents.6. Focus on Data Quality
Data integrity is essential throughout the analytical process. Prioritize thorough data validation to assure correctness and dependability, hence increasing stakeholder confidence and delivering actionable insights.7. Collaborate Effectively
Recognize that data analysis is a collaborative process. Cultivate good interpersonal skills to promote collaboration and harness the experience of others, resulting in deeper and higher-quality analysis.8. Continuously Reflect and Improve
Regularly reflect on previous analyses and solicit feedback to improve skills and techniques. Adopt a growth mentality and prioritize constant development to be competitive and successful in your data analyst profession.ReadMore ≫ How Medical Coding Jobs Can Change Your Life
Entry-Level Data Analyst Jobs
The followings are some typical job titles and descriptions for entry-level data analyst roles, which may vary based on the company and industry:
Internships provide hands-on experience with data analysis activities such as cleaning, visualizing, and basic statistical analysis. Interns may also help with report writing and presentation preparation to discuss findings.1. Data Analyst Intern
2. Junior Data Analyst
Typically, junior data analysts assist senior analysts with a range of data-related duties. Along with helping to create data models and reports, duties might involve gathering, cleaning, and analyzing data.3. Data Research Assistant
To assist research projects or corporate activities, this function entails gathering, organizing, and analyzing data from many sources. Database upkeep and literature reviews are other tasks that research assistants could be assigned.4. Data Entry Analyst
Data entry analysts at the entry level are in charge of entering and confirming information into spreadsheets or databases. Strong precision in data entry and attention to detail are necessary for this profession.5. Reporting Analyst
The primary goal of reporting analysts is to measure key performance indicators (KPIs) and give stakeholders insights by developing and managing reports and dashboards. Helping with presenting information and report creation may be part of entry-level jobs.6. Business Intelligence Analyst
Business intelligence analysts at the entry level assist with the creation and upkeep of tools and systems for business intelligence. They might help with database queries, data modeling, and insight generation to support decision-making procedures.7. Market Research Analyst
Analysts who specialize in market research gather and examine information on consumer behavior, market trends, and competitive environments. Helping with data collecting, analysis, and reporting duties to support market research initiatives may be part of entry-level jobs.Data Analyst Interview Questions
The following are a few typical questions asked during a data analyst interview:- Can you walk me through your experience with data analysis and any relevant projects you've worked on?
- How do you approach a new dataset or problem when starting an analysis?
- What tools and programming languages are you proficient in for data analysis?
- Can you explain the process you follow for data cleaning and preprocessing?
- How do you handle missing or incomplete data in your analyses?
- Can you describe a time when you had to present your findings from a data analysis to non-technical stakeholders?
- What data visualization techniques do you use to communicate insights effectively?
- Have you worked with any machine learning algorithms or predictive modeling techniques? If so, can you provide an example?
- How do you ensure the accuracy and reliability of your analysis results?
- Can you discuss a challenging problem you encountered during a data analysis project and how you approached solving it?
- How do you stay updated with the latest trends and advancements in data analysis and related technologies?
- Can you explain the difference between descriptive and inferential statistics, and when you would use each?
- How do you prioritize tasks and manage your time effectively when working on multiple projects simultaneously?
- Have you ever encountered ethical dilemmas in your work as a data analyst? How did you handle them?
- Can you provide an example of a successful data-driven decision or project that you contributed to?
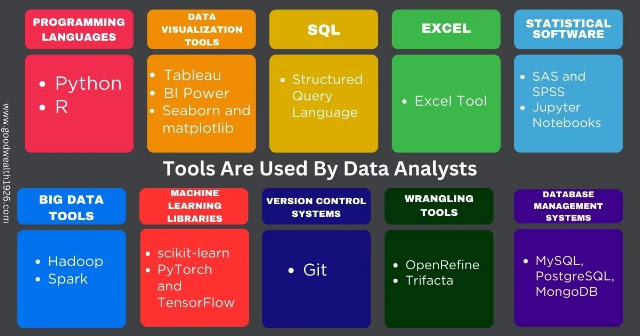
What Tools Are Used By Data Analysts?
A range of tools are used by data analysts to carry out their work quickly and effectively. Among the instruments that are most frequently used include:1. Programming Languages
- Python: Because of its many libraries, including Pandas, NumPy, and sci-kit-learn, it is widely used for data analysis, manipulation, and modeling.
- R: Because of its extensive collection of packages for statistical analysis and visualization, it is well-liked by statisticians and data miners.
2. Data Visualization Tools
- Tableau: Well-known for its intuitive user interface and potent graphical tools, which enable analysts to produce smart and dynamic illustrations.
- BI Power: Using various data sources, Microsoft's business analytics solution generates interactive reports and dashboards.
- Seaborn and matplotlib: Python packages that enable the direct creation of both dynamic and static depictions from data structures.
3. SQL
- Relational databases are popular data sources for analysts, and searching and manipulating them requires the use of Structured Query Language.
4. Excel
- Excel is still a popular tool for basic data analysis, reporting, and visualization even if it's not as advanced as other programs.
5. Statistical Software
- SAS and SPSS: Statistical software programs are frequently used for sophisticated statistical analysis in academics and some sectors.
- Jupyter Notebooks: An online application that is available as open-source software that enables users to generate and distribute documents with interactive code, equations, graphics, and narrative prose.
6. Big Data Tools
- Hadoop: A distributed framework for processing and storing massive amounts of data.
- Spark: A single, integrated analytics engine that supports streaming data, SQL, machine learning, and graph processing for handling massive amounts of data.
7. Machine Learning Libraries
- scikit-learn: Python package for machine learning applications, including dimensionality reduction, clustering, regression, and classification.
- PyTorch and TensorFlow: Neural network construction and training using deep learning frameworks.
8. Version Control Systems
- Git: A must for group projects and for monitoring modifications to analytic scripts and code.
9. Data Cleaning and Wrangling Tools
- OpenRefine: A free and open-source program for converting and cleaning unclean data.
- Trifacta: Data preparation and wrangling platform that automates repetitive operations and makes transformation suggestions.
10. Database Management Systems
- MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and so forth: Analysts may use a variety of database systems for data archiving, retrieval, and modification, depending on the kind of data.
How Much Does a Data Analyst Make?
Data analysts are expected to make an annual salary ranging from $60,000 to $150,000, based on location, experience, sector, and specialized abilities.Entry-level roles may pay between $60,000 and $80,000, but experienced professionals with sought-after knowledge or who work in high-demand sectors may earn more than $100,000 to $150,000.
These values are average and sensitive to market risk. Keeping up with current market trends and gaining relevant certifications or postgraduate degrees might help one's earning potential in the dynamic profession of data analysis.
Difference Between Data Analyst And Aata Scientist
Data Analyst and Data Scientist are two separate jobs in the field of information science, each with a unique set of responsibilities and qualifications. Following is an overview of the main differences between them.| Data Analyst | Data Scientist |
|---|---|
| The primary focus is on gathering, processing, and analyzing data to get insights and guide decision-making. They frequently deal with organized data and use statistical approaches to analyze trends and patterns. | Data insights are extracted using advanced statistical analysis, machine learning, and predictive modeling. To address difficult issues, they dive into complicated data sets, construct algorithms, and build prediction models. |
| Skilled with SQL, Excel, graphical data visualization tools such as Tableau or Power BI, statistical analysis methodologies, and fundamental programming languages such as Python or R. | Skilled in programming languages such as Python and R, methods for machine learning, statistical modeling, data mining, big data systems such as Hadoop and Spark, and sophisticated data graphing techniques. |
| Excel, SQL, Tableau, and Power BI are commonly used technologies for data cleansing and visualization. They can additionally use simple statistical tools such as SPSS or SAS. | Utilizes a broader range of tools and technologies including programming libraries like pandas, sci-kit-learn, TensorFlow, or PyTorch for machine learning, and frameworks for big data processing like Apache Spark. They may also work with cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud for scalable computing. |
| Focuses on giving descriptive insights from data to help businesses make decisions. They frequently answer particular queries given by stakeholders using historical data analysis. | Conducts exploratory data analysis to reveal hidden patterns, trends, and relationships. They create predictive models to forecast future trends, find opportunities, and manage risks. |
| Typically involved in the analysis of historical and current data to give insights for operational decision-making and strategic planning. | Engages in a larger range of tasks such as data exploration, feature engineering, model selection and tuning, and machine learning model deployment in production systems. |
The Conclusion
Starting a career of how to become a data analyst with no experience may seem overwhelming, but it's fully possible with the appropriate mentality and approach. Individuals may lay a solid basis for success by concentrating on key skills such as data processing, statistical analysis, and data visualization.Furthermore, getting appropriate credentials, whether through online courses or formal education programs, can increase one's reputation and skill in the sector. However, the trip does not stop there. Actively looking for opportunities to apply newly gained information through internships, freelancing projects, or personal initiatives is critical for polishing skills and acquiring real-world experience.
Persistence and perseverance are essential components of success in this changing business. Embracing difficulties, remaining adaptive, and always extending one's skill set are critical for keeping ahead in the ever-changing field of data analytics. With persistence and a proactive approach, individuals may overcome initial challenges and pave the route for a meaningful and gratifying career in data analysis.
Persistence and perseverance are essential components of success in this changing business. Embracing difficulties, remaining adaptive, and always extending one's skill set are critical for keeping ahead in the ever-changing field of data analytics. With persistence and a proactive approach, individuals may overcome initial challenges and pave the route for a meaningful and gratifying career in data analysis.











Post a Comment